Reverse Geocoding
The reverse geocode uses a location to lookup addresses.
Naurt will return the closest address to the provided location. If additional matches are requested, they will be the second closest, third closest and so on.
Use Case
The use case for a reverse geocode is for when you do not have any address information. This would be, for example, if a user is clicking on a map to find nearby places.
If you would like an example of how this looks, you can log into your account on the dashboard. By clicking on the map, the orange dot represents the search location and then you will see the searched locations clustering around it. An example is below:
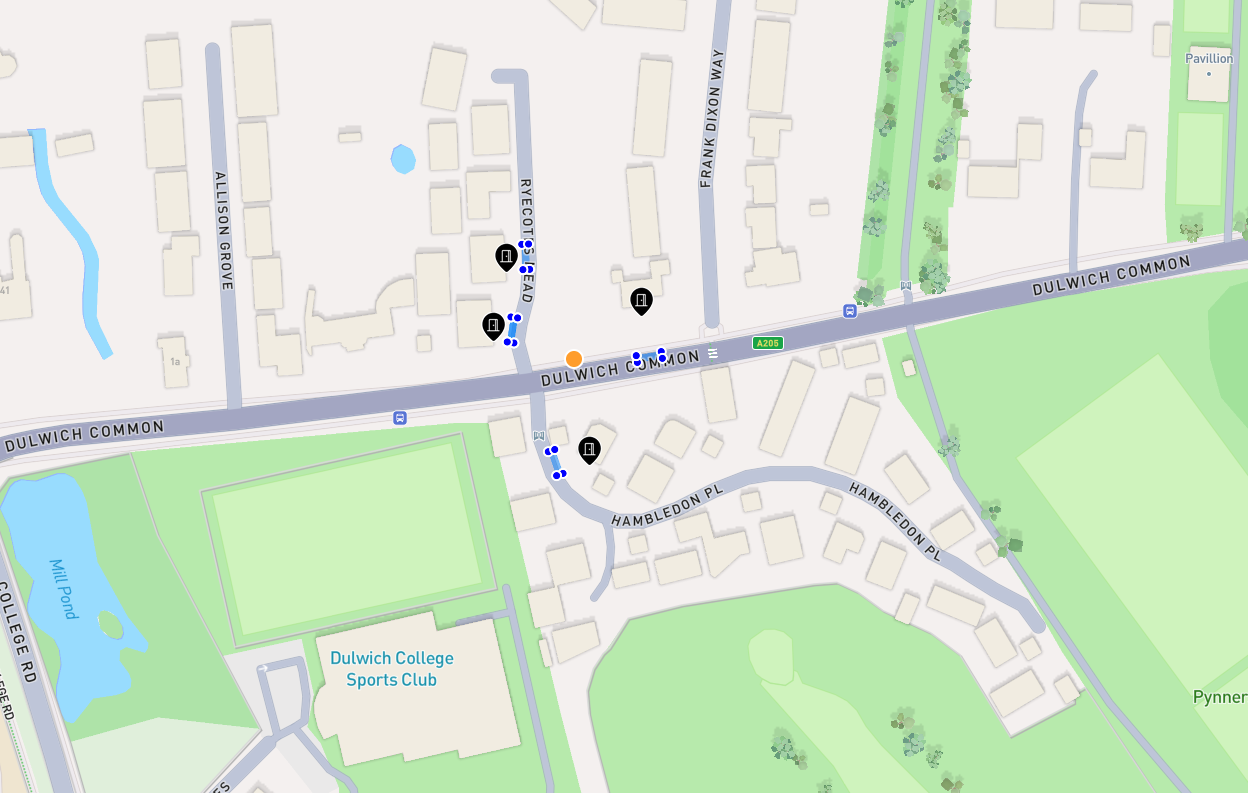
Examples
The example section shows the final JSONs which can be placed into the request queries list. It should be noted that a single request can contain multiple different kinds of queries.
Standard Reverse Geocode
{
"location": {
"latitude": 50.542,
"longitude": 0.234
}
}
Reverse Geocode with Distance Filter
{
"location": {
"latitude": 50.542,
"longitude": 0.234,
"distance_filter": 10000.0
}
}
Reverse Geocode with Additional Matches
{
"location": {
"latitude": 50.542,
"longitude": 0.234,
"distance_filter": 10000.0
},
"additional_matches": true
}
Restrictions
A reverse geocode request is incompatible with the id property.
If you use the address_string property too, then you are really doing a forward
geocode, and you can find those docs here.
If you use the address_structured property too, then you are really doing
a structured request, and you can find those docs here.
Language
When reverse geocoding, language can become a subtle point you may need to pay attention to. You can find out more about language options here